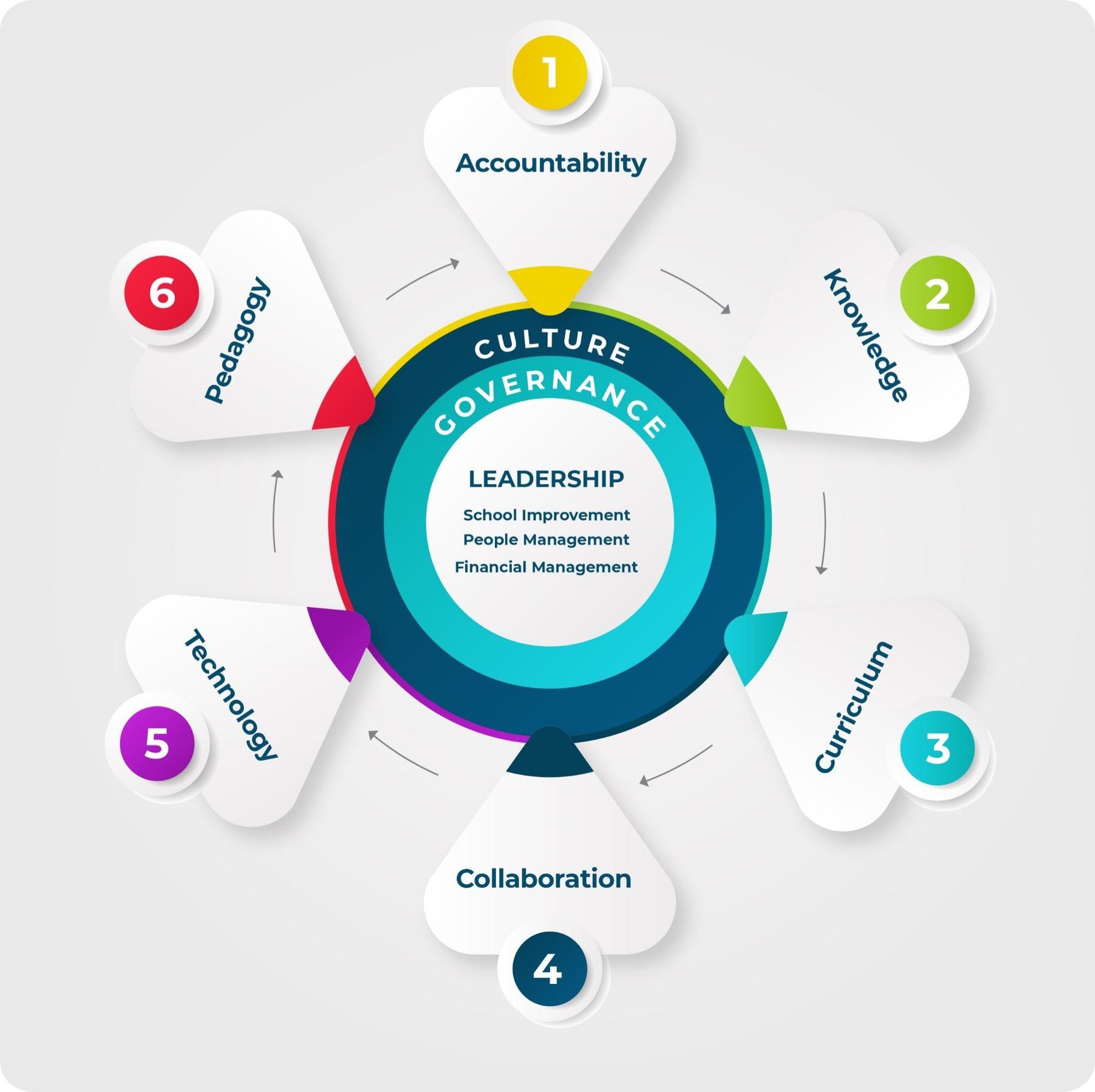
| CORE AREAS |
| Leadership |
- No shared vision or values exist
- Safeguarding concerns present
- Poor progress and outcomes
- Over-reliance on external support
- Inconsistent performance management
- Poor stakeholder communication
|
- Shared vision and values demonstrated
- Effective safeguarding arrangements
- Accurate improvement identification
- Clear accountability structures
- Consistent performance management
- Effective community engagement
|
- Values embedded in all decisions
- High-quality professional development
- Strategic stakeholder engagement
- Innovation and risk-taking encouraged
- System leadership contribution
- Distributed leadership excellence
|
| Governance |
- No unifying strategy or values
- Poor resource management
- Variable performance management
- Poor policy compliance
- No stakeholder consultation
- Skills gaps at multiple levels
|
- Coherent strategy in place
- Adequate resource management
- Systematic policy compliance
- Clear scheme of delegation
- Regular stakeholder communication
- Governance handbook established
|
- Deep stakeholder consultation
- Exceptional resource management
- Comprehensive impact evaluation
- Multi-stakeholder feedback systems
- Competency-based recruitment
- System leadership contribution
|
| Culture |
- No unifying values present
- Frequent bullying allegations
- Poor attendance (staff/pupils)
- High exclusion levels
- Elevated staff turnover
- Climate of fear and lack of innovation
|
- Shared values and expectations
- Improving educational outcomes
- National benchmark attendance
- Low exclusion levels
- Systematic CPD programme
- Earned autonomy and innovation
|
- Values demonstrated by everyone
- Elevated attendance levels
- Extremely low exclusions
- Systematic use of stakeholder voice
- Innovation actively encouraged
- Celebration systems embedded
|
| THE SIX LEVERS |
| Accountability |
- No clear accountability structures
- Poor data collection and analysis
- No stakeholder reporting
- Inconsistent intervention approaches
- External accountability seen as burden
- Poor financial accountability
|
- Clear accountability structures
- Regular performance monitoring
- Systematic intervention strategies
- Regular stakeholder reporting
- Some evaluation of initiatives
- Adequate financial oversight
|
- Accountability embedded in culture
- Strategic use of performance data
- Proactive issue identification
- Comprehensive stakeholder engagement
- Rigorous initiative evaluation
- Exemplary financial management
|
| Knowledge |
- No systematic data approach
- Data stored in silos
- Decisions not evidence-informed
- Limited data literacy
- Poor information governance
- No systematic learning from evidence
|
- Basic data collection systems
- Some evidence-informed decisions
- Growing data literacy
- Improving information governance
- Some evaluation taking place
- Technology systems integrating
|
- Sophisticated data systems
- All decisions evidence-informed
- High levels of data literacy
- Advanced analytics capabilities
- Exemplary information governance
- Strategic knowledge management
|
| Curriculum |
- No coherent curriculum vision
- Inconsistent planning approaches
- Limited progression consideration
- Curriculum doesn't meet all needs
- Assessment not aligned with intent
- Variable delivery quality
|
- Developing curriculum vision
- Some consistency in planning
- Some attention to progression
- Beginning to address different needs
- Some curriculum-assessment alignment
- Some enrichment opportunities
|
- Clear, ambitious curriculum vision
- Highly consistent planning
- Expertly designed for all pupils
- Assessment fully aligned
- Rich, varied enrichment
- Outstanding subject leadership
|
| Collaboration |
- Little or no collaboration exists
- Staff work independently
- No formal partnerships
- Limited parent/community engagement
- Competitive rather than collaborative culture
- No resource or expertise sharing
|
- Some collaborative activities emerging
- Some practice sharing occurring
- Some partnerships developing
- Some professional learning communities
- Some cross-curricular work
- Culture becoming more collaborative
|
- Collaboration systematic and embedded
- Regular structured practice sharing
- Strategic value-adding partnerships
- Thriving professional communities
- Rich cross-curricular collaboration
- Strategic external collaboration
|
| Technology |
- Limited or outdated infrastructure
- Ad-hoc technology use
- Staff lack confidence/skills
- Limited pupil access
- No strategic planning
- Inadequate technical support
|
- Basic infrastructure in place
- Some technology integration
- Most staff have basic skills
- Some strategic planning
- Some use for administration
- Basic digital citizenship coverage
|
- Robust, reliable infrastructure
- Seamless technology integration
- All staff confident users
- Equitable access for all pupils
- Strategic planning aligned with vision
- Comprehensive digital citizenship
|
| Pedagogy |
- Inconsistent teaching methods
- Limited understanding of learning
- Assessment doesn't support learning
- Limited differentiation
- Ineffective feedback to pupils
- Subject knowledge gaps
|
- Some consistency in approaches
- Growing understanding of learning
- Assessment beginning to support learning
- Some differentiation taking place
- Some use of research evidence
- Growing repertoire of strategies
|
- Highly consistent, evidence-informed practice
- Deep understanding of learning science
- Assessment seamlessly supports learning
- Sophisticated differentiation
- Outstanding subject knowledge
- Extensive strategy repertoire
|